Automation has become a modern buzzword – in manufacturing, production, and general business operation. Investing in excellent control systems in any manufacturing process can boost output and precision even with less workforce.
Apart from the overreliance on computers that enhance the automated process’s decision making, sensors are equally significant in continuous data collection.
The rotary encoder is a significant example of such sensors. But, what are rotary encoders, and how do they work? Read on to learn more on this and why such sensors are vital in any automation process.
What Are Rotary Encoders?
Rotary encoders are sensors used in the detection of a rotating shaft’s movement or angular position. Such sensors are used to convert the shaft’s rotational motion into signals for transmission to the primary PLC system, where a specific algorithm is used to process the inputted information into an appropriate response.
The encoders employ diverse sensor technologies, each of which depends on its suitability for a given use case.
Rotary encoders are highly useful in commercial and industrial designs. They are essential in small and large platforms such as photographic lenses and radar applications, respectively.
How Rotary Encoders Work
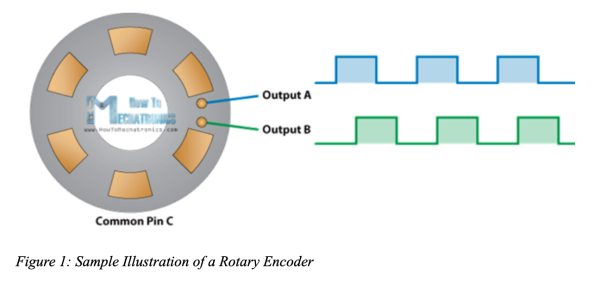
A rotary encoder contains several contact zones evenly distributed within a disk and linked to two contact pins – A and B, and a common pin C.
Figure 1: Sample Illustration of a Rotary Encoder
During rotation, the two separate pins – A and B make contact with pin C, generating output signals. The rotated position is determined based on the two outputs depending on the signal’s pulses.
In case the rotation of the direction is needed, the focus shifts to the simultaneous signals of both pins.
Rotary Encoders – Applications
Shaft encoders find use in all mechanical systems. These sensors are particularly prevalent within industrial settings that deal with delicate work, repeatable tasks, and prototyping that require high precision output.
- Encoders for Medical Industry: encoders are needed in the medical industry to enhance high precision, safe, and accurate tests and treatment. For instance, these sensors are applied in MRI scanning and CT machinery to guarantee patient safety and precise imaging.
- Technical: absolute encoders offer positioning data needed in technical applications such as in CNC machines. Each axis of motion comes with a full set of rotary encoders and actuators to enhance accuracy in the machining tool’s positioning.
- Mechanical: rotary sensors are commonly used within the manufacturing industry to automate critical tasks. For instance, in robotics, such sensors enhance the moving parts’ accurate positioning, direction, and speed.
Types of Rotary Encoders
Rotary encoders are available in different types, with the common ones being absolute and incremental sensors.
Incremental encoders are used in the measurement of positional changes instead of on the absolute position. Usually, such sensors will measure the changes from 0 after power is restored and often offer a continuous stream of data.
Absolute encoders can measure the shaft’s absolute position. These encoders do not rely on the point of reference. They are often used to provide data on direction, position, and speed.
Rotary encoders are a critical element of the automation process. Maintain the accuracy and precision you need by using the right sensors. Get in touch with European Technical Sales for procurement of rotary encoders.


Recent Comments